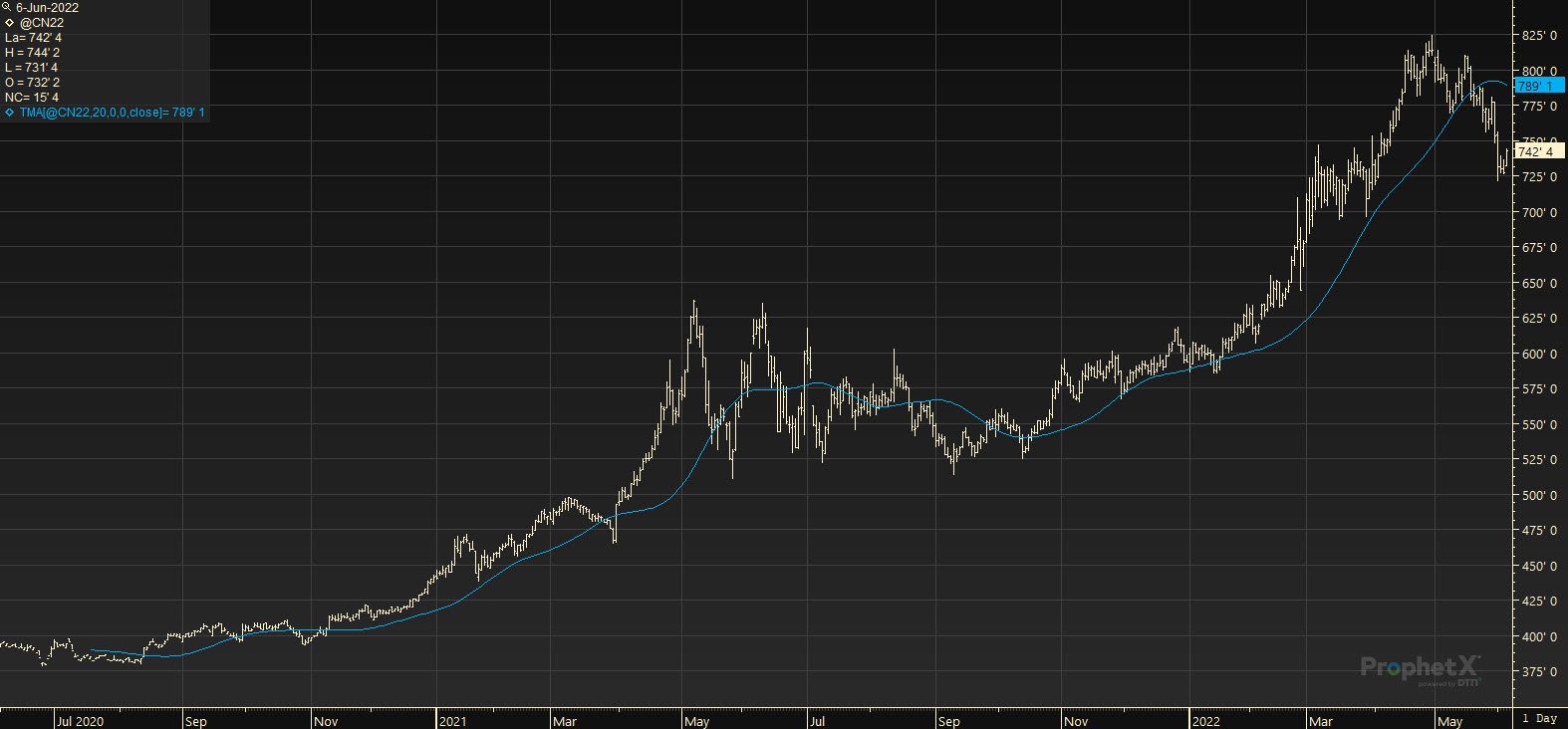
- Is a simple moving average that has been averaged again (i.e., averaging the average). This creates an extra smooth moving average line.
- The triangular moving average (TMA) shows the average price of an asset over a specified number of data points—usually a number of price bars.
- The purpose of the TMA is to double-smooth the price data, which will produce a line that doesn’t react as quickly as a simple moving average would.
- The TMA won’t react quickly in volatile market conditions, meaning that it will take longer for your TMA line to change direction.