A moving average is a simple average of data from a previous period. Its primary function is to identify changes in trends.
For Vert Shift% , enter the percentage to be added to or subtracted from the data points in the moving average line. If you enter a percentage of 1.00, for example, a point that would have been displayed at 200.00 will now be displayed 1% higher, at 202.00.
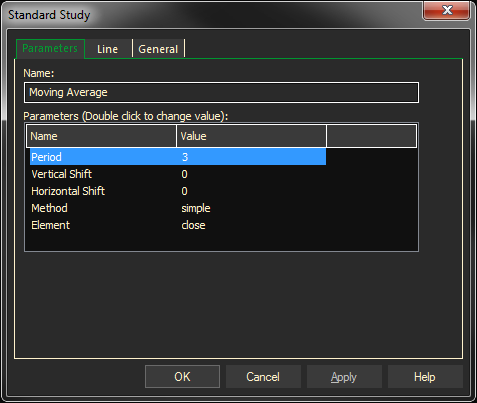
Parameters:
Symbol — data source symbol.
Period — time interval for moving average calculation
Vertical Shift % — moving average offset factor
Horizontal Shift — moving average offset factor
Method — moving average calculation method : (Simple, Exponential, Weighted, Smoothed)
Element — price field to use for calculation (Close, High, Low, Open)
Adding the Moving Average Study to a Chart
- Click on the f(x) Studies docked pane window.
- Click on the plus sign to expand the fx Standard.
- Find the Moving Average study, drag and drop it on the chart
Or
- Right-Click on a blank part of the chart and select ADD STUDY.
- Under Data Source, you will find a list of charts and studies in the window. Select the one on which you want the new study to be based.
- Under Studies, select the study you want to add to the window. The library of studies will include standard ProphetX studies plus those that you have created. The Most Recent will include studies that you have previously used.
- Under Add To, select the stack you want to add the study to, or select <New Stack> to create a new stack for the study.
- Click OK to exit.
Changing Parameters
Do either of the following to change the parameters:
- For an existing study on a chart, right-click on the study and select PROPERTIES on the pop-up menu, and modify as necessary.
- Right-click on the study name listed in the f(x) docked pane and make the changes in the displayed dialog. Update will save the parameters permanently.
Method Calculations for Moving Average
When a study is based on a moving average, Method (the method of calculation) is included as a parameter.
- Standard = 0 – the standard moving average calculates the arithmetic mean of a series of prices.
- Exponential = 1 – the exponential moving average gives less recent data progressively less weight.
- Weighted = 2 – the weighted moving average gives more weight to recent data using a linearly weighted ramp.
- Running = 3 – the running moving average uses only the previous position moving average and the current data to calculate each new position.